December 19, 2023
What materials are used in car suspension?
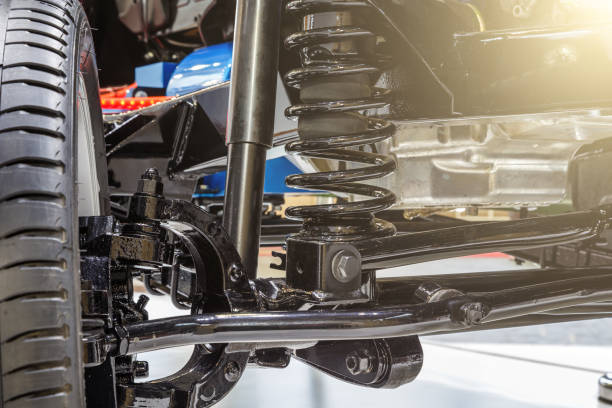
Car suspensions are made up of several components, and various materials are used to construct these components to provide the necessary strength, durability, and flexibility required for a vehicle’s suspension system. Some of the common materials used in car suspensions include:
- Steel: Steel is one of the most common materials used for suspension components such as coil springs, leaf springs, control arms, and some types of sway bars. It offers high strength and durability, which is crucial for these load-bearing parts.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is used in various suspension components to reduce weight while maintaining strength. Lightweight aluminum is often employed in control arms, subframes, and some suspension linkage parts.
- Rubber: Rubber bushings are used extensively in suspension systems to provide cushioning, reduce noise, and isolate vibrations. Rubber is flexible and helps absorb shocks and vibrations, enhancing ride comfort.
- Polyurethane: Polyurethane is another material used for bushings and suspension components. It offers better performance characteristics than rubber, including improved durability and resistance to wear and tear.
- Composite materials: Some high-performance and luxury vehicles use composite materials like carbon fiber or fiberglass in specific suspension components to reduce weight while maintaining strength and rigidity.
- Cast iron: Some older vehicles may still use cast iron for certain suspension components like steering knuckles or differential housings due to its durability and strength.
- Plastic and thermoplastic materials: Plastics and thermoplastics can be used in non-structural suspension components like control arm covers or dust shields due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
- High-strength alloys: Modern high-performance and sports cars may use advanced alloys such as high-strength steel, titanium, or magnesium in specific suspension components to reduce weight and improve handling characteristics.
- Rubber compounds with additives: Rubber used in suspension components may be mixed with various additives and compounds to enhance specific properties like heat resistance, vibration dampening, or durability.
- Fluids and hydraulic components: Hydraulic fluids and seals are used in shock absorbers and struts to provide damping and control over the vehicle’s ride quality.
The choice of materials for car suspension components depends on various factors, including the vehicle’s intended use, cost considerations, and the desired balance between ride comfort, handling, and durability. Manufacturers carefully select materials to meet these requirements while also adhering to safety standard.
How are car suspension made?
Car suspensions are made up of various components, each of which is manufactured using specific processes and materials. Here is an overview of how car suspensions are typically made:
- Design and Engineering:
- The suspension system is first designed by automotive engineers to meet the vehicle’s requirements for ride comfort, handling, and safety.
- Computer-aided design (CAD) software is often used to create detailed plans and specifications for each suspension component.
- Material Selection:
- The appropriate materials for each suspension component are selected based on factors such as strength, weight, durability, and cost.
- Component Manufacturing:
- Coil Springs: Coil springs are typically made from high-strength steel wire. The wire is coiled and heat-treated to achieve the desired spring rate and durability.
- Leaf Springs: Leaf springs consist of multiple layers of spring steel or composite materials. These layers are shaped, stacked, and clamped together with bolts or rivets.
- Control Arms: Control arms are usually fabricated from steel or aluminum. They are cut, bent, and welded into their specific shapes.
- Shock Absorbers and Struts: Shock absorber and strut components are manufactured separately and then assembled. These components include piston rods, dampening chambers, and valves.
- Bushings: Rubber or polyurethane bushings are molded into their desired shapes.
- Assembly:
- The individual suspension components, including control arms, springs, shock absorbers, sway bars, and bushings, are assembled into subassemblies or modules.
- These subassemblies are then installed into the vehicle’s chassis, typically on the front and rear axles.
- Quality Control:
- Quality control measures are in place at various stages of production to ensure that each component meets the required specifications for strength, dimensions, and durability.
- Suspension components are also subjected to testing to evaluate their performance and functionality.
- Installation:
- The fully assembled suspension system is installed in the vehicle, with each component connected to its respective mounting points on the chassis and axles.
- Precise alignment and torque specifications are followed during installation to ensure proper suspension geometry.
- Testing and Tuning:
- After installation, the suspension system is tested on a variety of surfaces and under different driving conditions to fine-tune the ride comfort and handling characteristics.
- Any necessary adjustments or modifications are made to achieve the desired ride quality and performance.
- Final Inspection:
- The completed vehicle undergoes a final inspection to ensure that the suspension system and all its components are functioning correctly and safely.
It’s important to note that the manufacturing process can vary depending on the type of suspension system (e.g., independent suspension, solid axle suspension, air suspension) and the specific design of the vehicle. Additionally, advancements in technology and materials have led to more sophisticated and lightweight suspension components in modern cars.