June 11, 2023
Automatic Transmission Fluid Service
Automatic transmission fluid (ATF) service refers to the maintenance and replacement of the fluid in an automatic transmission system. ATF plays a crucial role in lubricating the transmission’s moving parts, cooling the transmission, and facilitating smooth gear shifting.
Over time, ATF can break down due to heat and friction, losing its ability to perform these functions effectively. Regular ATF service helps maintain the transmission’s performance and extends its lifespan. Here are a few key points about automatic transmission fluid service:
- Fluid Inspection: During an ATF service, the technician inspects the fluid for signs of contamination, such as debris, metal shavings, or discoloration. These can indicate internal transmission problems that may require further investigation.
- Fluid Drain and Replacement: The old ATF is drained from the transmission pan or through a specialized machine that flushes the system. The pan gasket and filter may also be replaced, depending on the manufacturer’s recommendations. Then, fresh ATF is added to the appropriate level.
- Fluid Type and Specifications: It’s crucial to use the correct type of ATF recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Different transmissions may require specific fluid formulations, such as Dexron, Mercon, or CVT fluid. Using the wrong ATF can lead to transmission damage.
- Service Intervals: The recommended service intervals for ATF replacement vary depending on the vehicle and driving conditions. Generally, it’s advised to have the ATF serviced every 30,000 to 60,000 miles or every 2 to 4 years. However, it’s important to consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual for the manufacturer’s specific guidelines.
- Transmission Flush: Some service providers offer a transmission flush, which involves using a machine to remove old fluid while simultaneously adding new fluid. This process aims to remove more of the old fluid from the transmission and may be recommended in certain situations. However, it’s important to note that not all vehicles require a flush, and it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Professional Service: ATF service can be a complex procedure that requires specific tools and expertise. It’s generally recommended to have the service performed by a qualified technician or at a reputable automotive service center to ensure the job is done correctly.
Regular ATF service is essential for maintaining the health and performance of your vehicle’s automatic transmission. By following the manufacturer’s recommendations and addressing any signs of transmission problems promptly, you can help prevent costly repairs and ensure smooth and reliable operation of your vehicle.
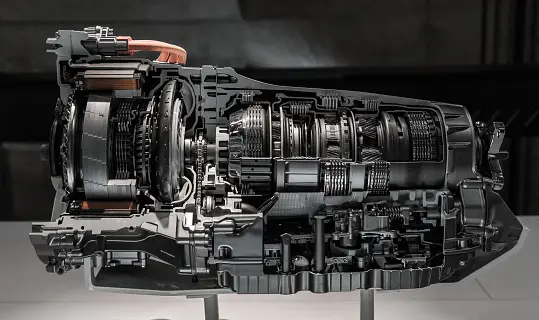
How often do you need to change automatic transmission fluid?
The frequency of automatic transmission fluid (ATF) changes can vary depending on several factors, including the vehicle’s make, model, and driving conditions. It’s essential to consult the specific recommendations outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual. However, as a general guideline, here are some common intervals for ATF changes:
- Every 30,000 to 60,000 Miles: Many manufacturers recommend changing the ATF every 30,000 to 60,000 miles (or approximately every 2 to 4 years) under normal driving conditions. This interval is suitable for most vehicles and helps maintain optimal performance.
- Severe Driving Conditions: If you frequently engage in severe driving conditions, such as towing heavy loads, driving in stop-and-go traffic, or operating in hot climates, you may need to change the ATF more frequently. Severe conditions can cause increased heat and strain on the transmission, leading to faster fluid degradation. In such cases, the interval may be reduced to 15,000 to 30,000 miles.
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations specific to your vehicle. They may provide specific guidance on ATF change intervals based on the transmission design, fluid type, and other factors. The owner’s manual will outline the manufacturer’s preferred maintenance schedule for your vehicle.
It’s important to note that some newer vehicles may have sealed transmissions that are not designed to have the ATF changed as a regular maintenance procedure. In these cases, the manufacturer’s recommendations should be followed.
Regularly changing the ATF is crucial to ensure proper lubrication, cooling, and overall longevity of the transmission. Neglecting ATF changes can lead to increased friction, heat buildup, and potential transmission damage. If you are unsure about the appropriate ATF change interval for your vehicle, consult with a qualified technician or contact the vehicle manufacturer for specific guidance.
Is it good to change automatic transmission fluid?
Yes, it is generally beneficial to change automatic transmission fluid (ATF) at regular intervals as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Here are some reasons why changing ATF is considered good for your vehicle:
- Maintains Transmission Performance: ATF serves multiple purposes in an automatic transmission system, including lubricating moving parts, cooling the transmission, and facilitating smooth gear shifting. Over time, ATF can break down due to heat and friction, losing its effectiveness. Regularly changing the ATF helps ensure that these functions are performed optimally, maintaining the transmission’s performance and preventing potential issues.
- Extends Transmission Lifespan: Clean and properly functioning ATF helps reduce wear and tear on transmission components, such as gears, clutches, and seals. By regularly changing the ATF, you can remove contaminants and prevent the accumulation of debris that may cause damage to these components. This, in turn, can extend the lifespan of your transmission and help avoid costly repairs or replacements.
- Improves Fuel Efficiency: A well-maintained transmission with clean ATF can contribute to better fuel efficiency. As the transmission operates smoothly and efficiently, it reduces power losses and allows the engine to work optimally. This can result in improved fuel economy and savings at the pump.
- Prevents Transmission Problems: Neglected or degraded ATF can lead to various transmission problems, including poor shifting, slipping gears, overheating, and even complete transmission failure. By changing the ATF regularly, you can prevent or minimize the likelihood of such issues, ensuring the reliability and longevity of your transmission.
- Detects Potential Issues: During an ATF change, a qualified technician may inspect the old fluid for signs of contamination or wear. This examination can help identify potential transmission problems or internal issues that may require further investigation and repairs. Early detection and resolution of problems can save you from more extensive and costly transmission repairs down the line.
It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended intervals and use the correct type of ATF for your specific vehicle. If you are unsure about the appropriate ATF change procedure or interval, consult the owner’s manual or seek advice from a qualified technician or automotive service center.
How do I keep my automatic transmission healthy
To keep your automatic transmission healthy and maintain its optimal performance, here are some essential tips:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual. This typically includes regular inspections, fluid changes, and other service intervals specific to your transmission.
- Check ATF Level and Quality: Periodically check the ATF level using the dipstick (if equipped) or the vehicle’s onboard system. Ensure that the fluid is at the proper level and inspect its color and consistency. If the ATF appears discolored, has a burnt smell, or contains debris, it may indicate a problem and warrant further investigation.
- Use the Correct ATF: Always use the ATF type specified by the vehicle manufacturer. Different transmissions require specific fluid formulations, such as Dexron, Mercon, or CVT fluid. Using the wrong ATF can lead to transmission issues or even damage.
- Avoid Overloading or Overheating: Avoid exceeding the recommended load limits of your vehicle, as overloading can put excessive strain on the transmission. Additionally, excessive heat can degrade ATF and harm the transmission. If you frequently engage in activities like towing or driving in hot climates, consider using additional cooling systems or transmission coolers.
- Warm Up Before Driving: Give your vehicle a few minutes to warm up before driving, especially in cold weather. This allows the ATF to reach its optimal operating temperature, ensuring smoother gear shifts and reduced strain on the transmission.
- Practice Smooth Driving: Avoid sudden and aggressive acceleration or braking, as these actions can put stress on the transmission. Smooth and gradual acceleration, as well as coasting to a stop whenever possible, helps minimize wear and tear on the transmission components.
- Service Transmission Fluid Regularly: Follow the recommended intervals for changing the ATF. Regular fluid changes help remove contaminants, debris, and old fluid that can negatively impact the transmission’s performance.
- Address Problems Promptly: If you notice any signs of transmission issues, such as slipping gears, rough shifting, or unusual noises, have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician. Addressing problems early can prevent further damage and potentially save you from costly repairs.
Remember, each vehicle and transmission may have specific requirements, so consulting your owner’s manual and following the manufacturer’s recommendations is crucial for maintaining a healthy automatic transmission. Regular maintenance, proper driving habits, and attentive care will contribute to the longevity and reliability of your transmission.
What kills automatic transmissions?
Several factors can contribute to the premature failure or damage of automatic transmissions. Here are some common factors that can negatively impact and potentially “kill” automatic transmissions:
- Lack of Proper Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance, such as not changing the automatic transmission fluid (ATF) at recommended intervals, can lead to fluid degradation, inadequate lubrication, and increased wear on transmission components. Over time, this can result in poor performance, overheating, and transmission failure.
- Overheating: Excessive heat is a significant enemy of automatic transmissions. Driving under heavy loads, in extreme temperatures, or without proper cooling can cause ATF to break down, lose its lubricating properties, and increase friction in the transmission. Continuous exposure to high temperatures can lead to internal damage, including warped seals, worn clutches, and transmission slippage.
- Improper Fluid Levels: Insufficient or excessive ATF levels can cause problems. Low fluid levels can result in inadequate lubrication and insufficient hydraulic pressure, leading to slipping gears, overheating, and internal damage. Conversely, overfilling the transmission can cause foaming, fluid leakage, and increased pressure, potentially damaging seals and other components.
- Contaminated Fluid: Dirty or contaminated ATF can accelerate transmission wear. Contaminants such as dirt, debris, metal shavings, or moisture can impair the fluid’s lubricating properties, clog filters, and lead to increased friction and component damage.
- Incorrect Fluid Type: Using the wrong type of ATF or mixing different types can cause compatibility issues, leading to poor lubrication, reduced performance, and potential damage to seals, clutches, and other components.
- Severe Driving Conditions: Frequent exposure to severe driving conditions, such as towing heavy loads, driving in stop-and-go traffic, or operating in hilly terrain, can put significant stress on the transmission. Continuous strain can cause increased heat buildup, excessive wear on clutch plates, and other components, ultimately leading to transmission failure if not properly addressed.
- Improper Towing: Towing loads that exceed the vehicle’s recommended towing capacity or using improper towing techniques can place excessive strain on the transmission. Overloading the transmission can cause overheating, fluid degradation, and accelerated wear.
- Incorrect Shifting or Driving Habits: Abrupt and aggressive shifting, excessive gear hunting, frequent shifting between reverse and drive without coming to a complete stop, or riding the clutch can contribute to transmission wear and damage.
- Manufacturer Defects or Design Issues: In some cases, automatic transmissions may have inherent design flaws or manufacturing defects that can lead to premature failure. These instances are relatively rare but can occur, resulting in transmission problems.
It’s important to note that while these factors can increase the risk of transmission issues, proper maintenance, attentive driving habits, and regular inspections can help mitigate the risks and extend the lifespan of your automatic transmission.
